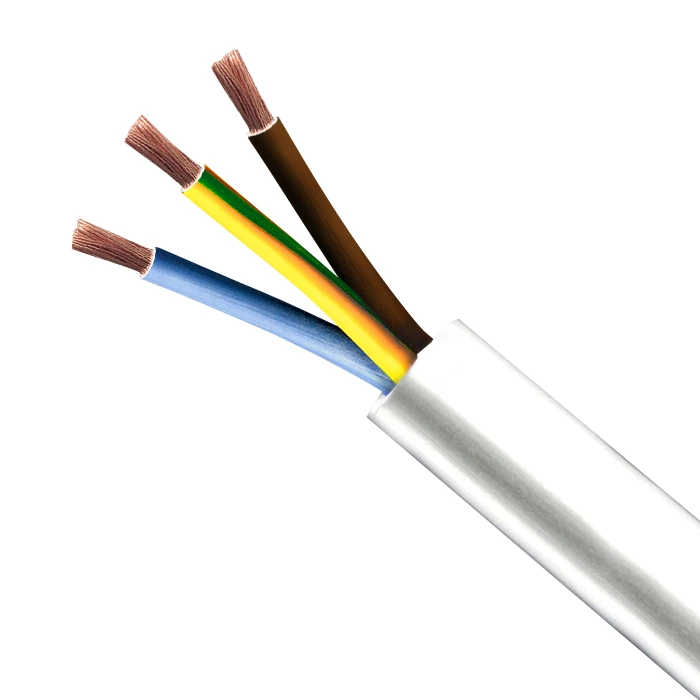
Electric wire-Copper/PVC
Application:
Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure.
Wiring is subject to safety standards for design and installation. Allowable wire and cable types and sizes are specified according to the circuit operating voltage and electric current capability, with further restrictions on the environmental conditions, such as ambient temperature range, moisture levels, and exposure to sunlight and chemicals.
Model No.:Electric wire
Material:Copper/PVC
Brand:KINGYEAR
Standard:ASTM/AS/BS/DIN/IEC/NFC
Place of Origin:China
Package:Exported Wooden Drum or soft roll
Range of Application:indoor
Terms of Payment: L/C, T/T, D/P, PayPal, Western Union, Small-amount payment
Certification:ISO,CE and other certifications.
Production Capacity:30000m/week
● Europe
In European countries, an attempt has been made to harmonise national wiring standards in an IEC standard, IEC 60364 Electrical Installations for Buildings. Hence national standards follow an identical system of sections and chapters. However, this standard is not written in such language that it can readily be adopted as a national wiring code. Neither is it designed for field use by electrical tradespeople and inspectors for testing compliance with national wiring standards. By contrast, national codes, such as the NEC or CSA C22.1, generally exemplify the common objectives of IEC 60364, but provide specific rules in a form that allows for guidance of those installing and inspecting electrical systems.
● Germany
The VDE is the organisation responsible for the promulgation of electrical standards and safety specifications. DIN VDE 0100 is the German wiring regulations document harmonised with IEC 60364. In Germany, blue can also mean phase or switched phase.
● United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, wiring installations are regulated by the Institution of Engineering and Technology Requirements for Electrical Installations: IEE Wiring Regulations, BS 7671: 2008, which are harmonised with IEC 60364. The 17th edition (issued in January 2008) included new sections for microgeneration and solar photovoltaic systems. The first edition was published in 1882. In 2018, the 18th edition of the wiring regulations BS7671:2018 was released and came into force in January 2019 and BS7671:2018 Amendment 2 was issued March 2022. BS 7671 is the standard to which the UK electrical industry adheres, and compliance with BS 7671 is now required by law through the Electricity, Safety, Quality and Continuity Regulations 2002.
● North America
Further information: Electric power distribution § Secondary distribution, and Electrical wiring in North America
The first electrical codes in the United States originated in New York in 1881 to regulate installations of electric lighting. Since 1897 the US National Fire Protection Association, a private non-profit association formed by insurance companies, has published the National Electrical Code (NEC). States, counties or cities often include the NEC in their local building codes by reference along with local differences. The NEC is modified every three years. It is a consensus code considering suggestions from interested parties. The proposals are studied by committees of engineers, tradesmen, manufacturer representatives, fire fighters, and other invitees.
Since 1927, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) has produced the Canadian Safety Standard for Electrical Installations, which is the basis for provincial electrical codes. The CSA also produces the Canadian Electrical Code, the 2006 edition of which references IEC 60364 (Electrical Installations for Buildings) and states that the code addresses the fundamental principles of electrical protection in Section 131. The Canadian code reprints Chapter 13 of IEC 60364, but there are no numerical criteria listed in that chapter to assess the adequacy of any electrical installation.
Although the US and Canadian national standards deal with the same physical phenomena and broadly similar objectives, they differ occasionally in technical detail. As part of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) program, US and Canadian standards are slowly converging toward each other, in a process known as harmonisation.
● Europe
As of March 2011, the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) requires the use of green/yellow colour cables as protective conductors, blue as neutral conductors and brown as single-phase conductors.
● Sweden
In Sweden, IEC 60364 is implemented through the national standard SS-436 40 000. Notable is the exception for blue, where while the colour normally is used for neutral may be used as connecting wire between switches and between switch and fixture, as well as phase wire in a two-phase circuit, all under the condition that no neutral wire is used in the particular circuit.
● United Kingdom
Main article: Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom requires the use of wire covered with green/yellow striped insulation, for safety earthing (grounding) connections. This growing international standard was adopted for its distinctive appearance, to reduce the likelihood of dangerous confusion of safety earthing (grounding) wires with other electrical functions, especially by persons affected by red–green colour blindness.
In 2004, the UK adopted the European Union standard for phase colours of brown, black, and grey, and for neutral, blue. However, the old phase colours of red, yellow, and blue with black for neutral are still found in old installations. Single-phase wiring should strictly be in brown (red in old system), regardless of which phase it originated from, but it is common practice to use three-core cable in the three-phase colours for two-way lighting switches. The accepted practice is to sleeve the ends of the cores in brown or blue sleeves as appropriate.
● United States
Main article: Electrical wiring in North America
The United States National Electrical Code requires a bare copper, or green or green/yellow insulated protective conductor, a white or grey neutral, with any other colour used for single phase. The NEC also requires the high-leg conductor of a high-leg delta system to have orange insulation, or to be identified by other suitable means such as tagging. Prior to the adoption of orange as the suggested colour for the high-leg in the 1971 NEC, it was common practice in some areas to use red for this purpose.
The introduction of the NEC clearly states that it is not intended to be a design manual, and therefore creating a colour code for ungrounded or "hot" conductors falls outside the scope and purpose of the NEC. However, it is a common misconception that "hot" conductor colour-coding is required by the Code.
In the United States, colour-coding of three-phase system conductors follows a de facto standard, wherein black, red, and blue are used for three-phase 120/208-volt systems, and brown, orange or violet, and yellow are used in 277/480-volt systems. (Violet avoids conflict with the NEC's high-leg delta rule.) In buildings with multiple voltage systems, the grounded conductors (neutrals) of both systems are required to be separately identified and made distinguishable to avoid cross-system connections. Most often, 120/208-volt systems use white insulation, while 277/480-volt systems use grey insulation, although this particular colour code is not currently an explicit requirement of the NEC.Some local jurisdictions do specify required colour coding in their local building codes, however.
KINGYEAR from 2013-2018 are mainly for domestic trading and processing to some export trading companies. The average sales amount are about RMB 320,000,000 per year. For cables oversea market, From last may till now we have expanded our market to Bolivia, Peru, Dominican, Philippines, Vietnam, Thailand, Iraq, Mongolia, Indonesia and some Africa country. With total sales amount over USD10,000,000.
Advantage
FAQ